
ABOUT XEPI®
(ozenoxacin)
CREAM, 1%
ABOUT XEPI®?
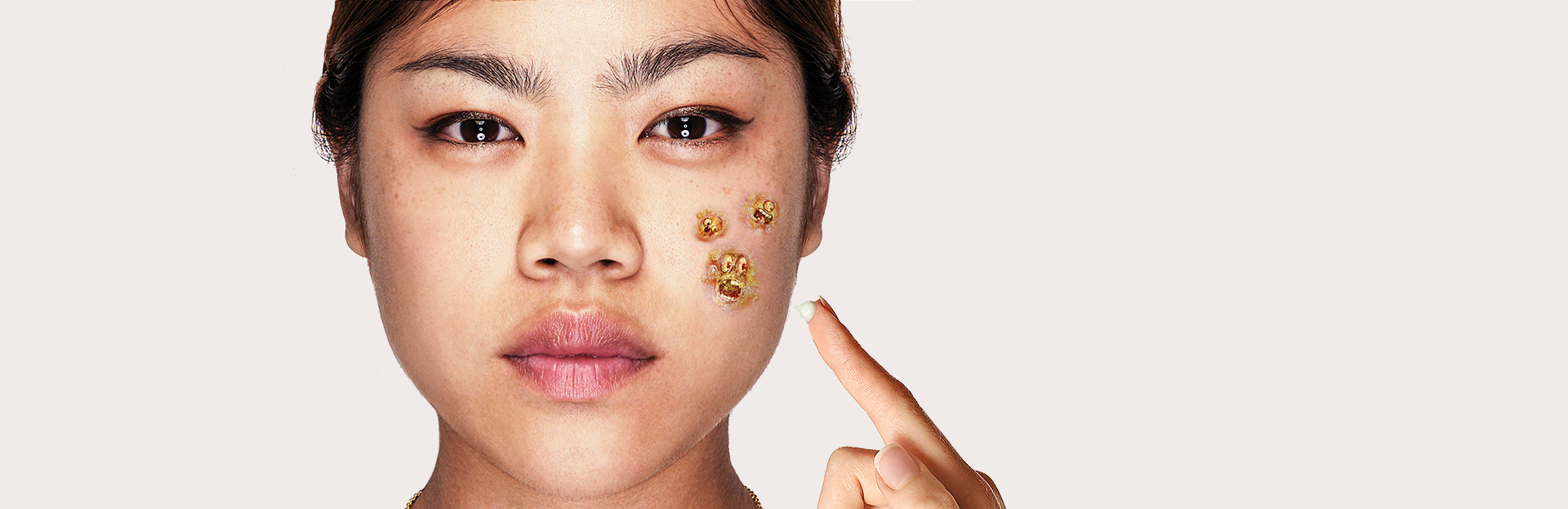
Xepi® is an antibiotic cream that treats impetigo (im-puh-TIE-go) by killing Staphylococcus aureus (STAFF-oh-low-cock-us ORE-ee-us) and Streptococcus pyogenes (STREP-toe-cock-us PIE-oj-en-eez) bacteria.1
- Antibiotics can be either bacteriostatic or bactericidal2
- Bacteriostatic drugs slow bacterial growth but do not kill bacteria
- Bactericidal drugs disrupt and kill bacteria cells

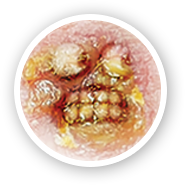
XEPI® HAS YOU COVERED BECAUSE ITS ACTIVE INGREDIENT, OZENOXACIN, IS BACTERICIDAL AND KILLS SUSCEPTIBLE STRAINS OF S. AUREUS AND S. PYOGENES THAT CAUSE IMPETIGO.3
- This includes activity against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in a laboratory setting1
XEPI® WORKS WITHIN DAYS TO GET YOU BACK TO YOUR NORMAL LIFE
- Clearance of impetiginous bacteria* was seen after 5 days of treatment twice a day4,5
- With substantial improvement as early as 2 to 3 days4,5
*Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
S. aureus; S. pyogenes
Medical studies compared the effect of Xepi® and a placebo cream (cream without the active drug) on impetigo in patients with S. aureus and/or S. pyogenes.1,4,5
Xepi® showed a significant improvement at the end of 5 days of therapy when compared to the placebo cream.1,4,5
Xepi® was tested in 2 medical studies that included 723 people aged 2 months or older. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either Xepi® or the placebo cream and did not know which cream they were given (blinded).1,4,5
They applied Xepi® or the placebo cream twice a day for 5 days. The affected body surface could not be larger than 2% for patients aged 2 months to 11 years.1,4,5
The percentage of patients with no more or fewer symptoms and not requiring additional antimicrobial therapy for the treated areas is shown in the table below, grouped according to the type of bacteria causing impetigo (S. aureus or S. pyogenes).1

Contact your doctor if your infection does not start to get better after 3 days1
HOW DO I USE XEPI®?1
Xepi® is a prescription drug approved for adults and children 2 months of age and older
Apply Xepi® in a thin layer twice per day, for 5 days, where impetigo sores are present
Do not use Xepi® if the affected area of impetigo is bigger than the size of the child’s two (2) hands (100 cm2)
Use Xepi® only on the skin. Don’t apply Xepi® in your eyes or body cavities (like your mouth or nose)
Wash your hands after applying Xepi® if hands are not the area being treated
Use Xepi® for the entire time recommended by your doctor, even when symptoms have improved
Always follow your doctor’s instructions
The prolonged use of Xepi® may result in hard-to-treat bacteria and fungi
- Talk to your doctor if your infection does not get better after 3 days
XEPI® SIDE EFFECTS

Xepi® was proven to be safe in studies of both adults and children 2 months of age and older.1
- Fewer than 1% of patients in clinical studies had side effects, which were:
- Rosacea, which is a skin condition that may include redness, flushing, and acne-like lesions
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which is a skin condition that causes scaly patches and red skin
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Uses: Xepi® is a topical prescription medicine approved for the treatment of impetigo, a skin infection caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and is approved for adults and children two months of age and older.
Warnings:
When using this product:
- Potential for Microbial Overgrowth: The prolonged use of Xepi® may result in hard-to-treat bacteria and fungi. Notify your healthcare practitioner if there is no improvement in symptoms within 3 days after starting use of Xepi®.
Most common side effects were:
- Rosacea (a skin condition that may include redness, flushing and acne-like lesions) and seborrheic dermatitis (a skin condition that causes scaly patches and red skin) were reported in 1 adult patient treated with Xepi®.
Pregnancy Warning: There is no available data on Xepi® use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk.
Lactation Warning: There is no available data regarding the presence of the active ingredient (ozenoxacin) in human milk, or the effects of ozenoxacin on the breastfed infant or on milk production.
Pediatric Warning: The safety and effectiveness of Xepi® in the treatment of impetigo have been established in patients 2 months to 17 years of age. The safety profile of Xepi® in patients 2 months and older was similar to that of adults.
The safety and effectiveness of Xepi® have not been established in patients younger than 2 months of age.
Geriatric Warning: Clinical studies of Xepi® did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and older to find out whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Directions:
- Use Xepi® for the entire time, as directed by your Health Care Provider.
- Do not use Xepi® if the affected area of impetigo is bigger than the size of the child’s two (2) hands.
- Xepi® is for external use only.
- Do not swallow Xepi® or use in the eyes, on the mouth or lips, inside the nose, or inside the female genital area. Wash your hands after application if hands are not the area for treatment.
Inactive Ingredients: benzoic acid, octyldodecanol, peglicol 5 oleate, pegoxol 7 stearate, propylene glycol, purified water, stearyl alcohol
Other Information:
- The risk information provided here is not comprehensive. To learn more, talk about Xepi® with your health care provider. The FDA approved product labeling can be found at https://www.xepicream.com/PI. You are encouraged to report side effects of Xepi®. Please contact Biofrontera Inc. at 1-844-829-7434 or FDA at 1-800-332-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
References: 1. Xepi® [package insert]. Woburn, MA: Biofrontera, Inc.; 2020. 2. Leeka S, Terrell CL, Edson RS. General principles of antimicrobial therapy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2011;86(2):156-167. 3. Canton R, Morrissey I, Vila J, et al. Comparative in vitro antibacterial activity of ozenoxacin against Gram-positive clinical isolates. Future Microbiol. 2018;13:3-19. 4. Gropper S, Albareda N, Chelius K, et al. Ozenoxacin 1% cream in the treatment of impetigo: a multicenter, randomized, placebo- and retapamulin-controlled clinical trial. Future Microbiol. 2014;9(9):1013-1023. 5. Rosen T, Albareda N, Rosenberg N, et al. Efficacy and safety of ozenoxacin cream for treatment of adult and pediatric patients with impetigo: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(7):806-813.